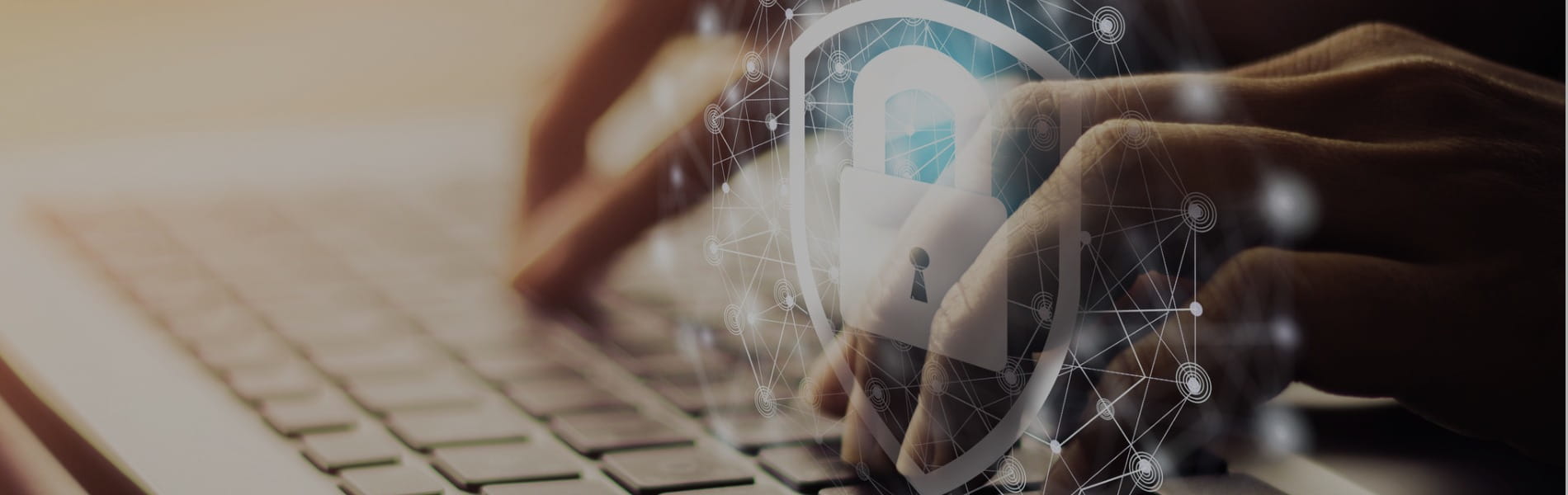
One of the most important aspects of any business is the security of data. Cyber Security is paramount to securing sensitive data or systems. This includes identifying and securing against common security issues such as code injection, data breaches, malware infection, DDoS, and even insider threats.
While a vast majority of cyber attacks come from external threats, there are occasions where sensitive information is under attack from within, which is often overlooked. And insider threats are on the rise, with the number of incidents increasing 47% over the last two years alone.
To ensure you are doing what you can to secure your data and that of your clients, let’s take a closer look at insider threats. We will specifically look at:
- What are insider threats?
- What are the types of insider threats?
- What are ways to prevent insider threats?
- What are ways to handle existing insider threats?
What are Insider Threats?
Insider threats are malicious threats perpetrated against a business or organization by someone with direct access to the organization. These types of threats are not merely the result of an employee’s actions. Former employees, business associates, and business contractors can have legitimate access to data, systems, and information posing a threat to a company.
There are several components to insider threats. They can include fraud, information or intellectual property theft, or destruction of computer systems.
The 3 Types of Insider Threats
Insider threats usually fall into one of three categories:
1. Malicious
Malicious insiders are those who take advantage of their direct access to inflict harm to an organization. Depending on the level of access the person has, these types of threats can be hazardous. The abuse of legitimate access would lead to non-public information used for unintended purposes. These are also known as turncloaks.
2. Negligence
Negligent insiders are people who make errors and disregard policies, placing their companies at risk. Hackers and other nefarious persons find it easier to find negligent employees than to poke holes in businesses’ security measures.
3. Infiltration
Infiltrators are those that act externally and obtain legitimate access to businesses without express authorization. While negligent insiders can play a part in these kinds of threats, Infiltrators can find other means of gaining access to sensitive information.
The 3 Indicators of Insider Threats You Can Track
Here are the 3 most common indicators to watch for concerning insider threats from employees, former employees, contractors, vendors, or partners:
- Access of Sensitive Information: Requesting or accessing information not typically accessed for their role in the organization, or crawling your networks for sensitive data.
- Downloading of Information: Downloading information onto unauthorized external storage devices, downloading large amounts of data, or copying files from folders containing sensitive information.
- Sending Information Outside Organization: Emailing or sending sensitive information to outside sources.
4 Ways to Prevent Insider Threats
Insider threat prevention is achievable with the right security measures implemented.
1. Securing Internal Network and Workstations
Data security starts with securing your internal network and employee workstations. Ensuring the protection of the equipment, software, and services used by employees is essential. Having a team of individuals armed with the proper software and know-how is critical to securing physical hardware and systems.
2. Backup Data
In addition to securing the data, it is equally as important to correctly backup data. Your business cannot afford to lose critical assets, so backups become a vital part of disaster recovery. Proper backups will help prevent loss of data should a threat delete retained information.
3. Secure Sensitive Files and Limit Access
Next, secure all sensitive files and limit access to them. Cybersecurity professionals accomplish this by using administrative tools for managing users. Companies should analyze logs and other data to monitor who is accessing or attempting to access sensitive information. Not only can you watch for malicious insiders, but also outsiders trying to gain access.
4. Train Employees on Policies
Business owners can also implement annual security awareness training to ensure that new and existing employees are abreast of existing policies and changes. Ongoing yearly and incremental training is a great way to keep security at the forefront of everyone’s minds. The education tools can be general as well as specific to common incidents occurring within an organization.

3 Steps to Immediately Handle Insider Threats
Even those with all of these security measures in place must still consider the possibility of insider threats and plan accordingly. Use these three steps to handle insider threats:
1. Identify Users and Affected Data
Once you have identified that a threat has happened, you need to identify the user(s) or affected data. It is good practice to log affected users out and restrict access until the resolution of the issue. If the attack was sophisticated with additional rights provided, revoke those privileges. The appropriate internal personnel should be alerted as well to take further action. You should also alert the authorities if necessary.
2. Check for and Remove Any Malware
Additional measures to take would be to check for the presence of any malware or other malicious software put in place to carry out future attacks. While the number of attacks declined year over year from 2018 to 2019, hackers carried out 9.9 million attacks in 2019. Powerful antivirus software will go a long way in securing your infrastructure.
3. Restore Deleted Data
Once you have gotten rid of any harmful software, restore any deleted data. Assuming proper backup solution implementation, maliciously deleted data is quickly restored.
Secure Your Infrastructure with Liquid Web’s Managed Hosting
Liquid Web has a myriad of built-in, server-side services to secure your hosted infrastructure. On a basic level, there are specific server security measures by default, which include:
- Firewall Protection
- Anti-Spam & Antivirus Protection
- HTTP Intrusion Protection
- Server Hardening
- Daily Security Audits
Additional security options exist for customers wanting to lock down their environment further. Contact us today to get more information.
Issues with Secure Infrastructure? Download our Security Infrastructure Checklist for SMBs.
[ad_2]
Source link